Neurobiological Foundations
This article is aimed at all those who are interested in the neurobiological effects of autogenic training and would like to learn more about it.
How was Autogenic Training developed?
The German neuropsychologist Johannes Heinrich Schultz developed Autogenic Training in the 1930s. He observed that he had patients who, through self-hypnosis, managed to bring themselves into a state that was previously only possible with a therapist experienced in hypnosis. The original autogenic training has since been adapted to incorporate the latest findings. While it was originally developed to support psychotherapeutic treatments for individuals with several types of illnesses, autogenic training is now also applied to healthy individuals.
The use of Autogenic Training by healthy people helps:
- to improve the quality of life
- to improve confidence and efficiency
- to increase athletic efficiency
- to learn and concentrate better
- to increase performance in various areas of work, etc.
Originally, Autogenic Training was considered the „little sister of psychotherapy.”
However, not because it could be used to provide general therapy talks (which is not possible), but because many people no longer needed psychotherapy after undergoing Autogenic Training!
The technique of self-hypnosis consists of three levels:
You will notice: Right after the first few sessions, Autogenic Training begins to take effect.
➔ The basic level is a physical relaxation method consisting of 6-8 consecutive exercises. Here, you learn to quiet your thoughts, train your body awareness and imagination, and deliberately influence bodily functions.
eg.: „My right arm is heavy. I’m calm and relaxed.”
➔ The intermediate level is a mental training with formulas for long-term self-influence. This level involves addressing individual problems and goals. You learn to create and apply your personal formulas – positive affirmations – to gradually shape your life according to your desires.
eg: „I’m full of energy. I’m worthy and lovable.”
➔ The advanced level is a self-hypnosis technique influencing one’s own subconscious. A thorough mastery of the basic stage is a prerequisite here. This form of autogenic training is depth-psychologically oriented and utilizes meditative techniques with the aim of looking inward, processing experiences, and experiencing oneself. It serves the development of creative resources. eg: „A picture is developing in my mind’s eye: I see and experience love.”
Neurobiological Foundations
What happens in the brain during autogenic training? The fundamental distinction in the locations of action between the basic, intermediate, and advanced levels is that in the basic level, the autonomic nervous system is influenced, while in the intermediate and advanced levels, the central nervous system, including the brain, our control center, is affected.
Effective approach for the Basic Level – Our Nervous Systems
At the basic level, the autonomic nervous system is trained. Anatomically, our nervous system comprises two major components. There is the central nervous system, which includes all nerve pathways in the brain and spinal cord.
It is nestled within our skull and the spinal canal of the spine. All other nerve pathways of the body belong to the peripheral nervous system.
On a functional level, there is a distinction between a voluntary and an involuntary, autonomic nervous system. The voluntary, also known as the somatic nervous system, controls all processes that we can consciously influence with our will. This includes targeted movements of the arms and legs.
In contrast, the autonomic, also referred to as the autonomous nervous system, regulates all non-voluntary processes in the body that occur independently of our consciousness. It is constantly active, regulating, among other things, respiration and the activity of internal organs.
It receives signals from the body and sends them to the brain, and vice versa, it forwards messages from the brain to the body, such as accelerating the heartbeat during excitement. Thus, the autonomic nervous system is very quickly able to adapt bodily functions to external conditions.
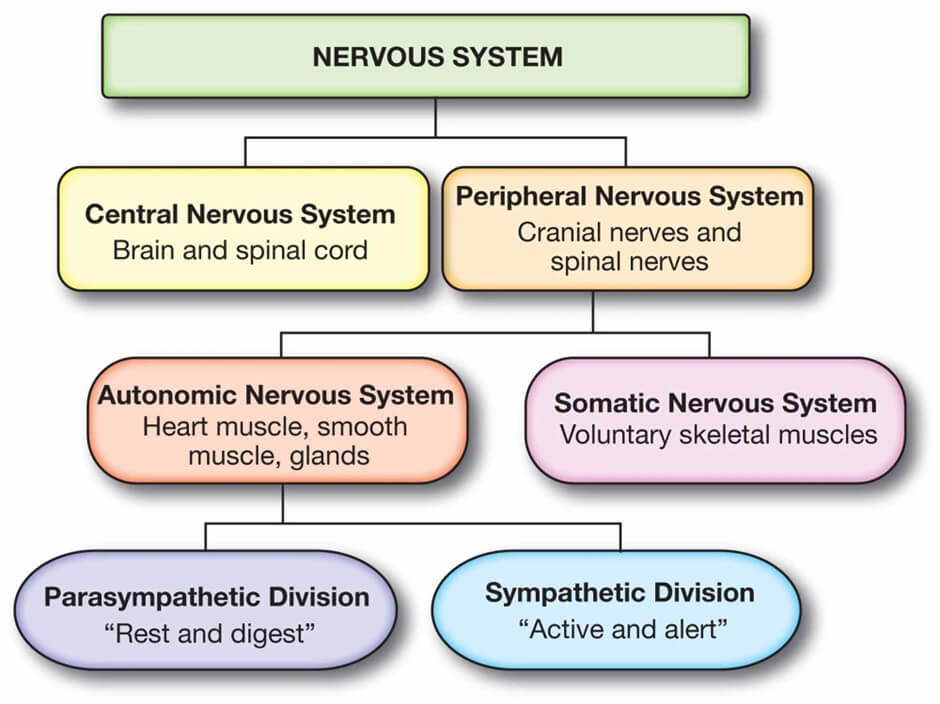
Sympathetic nervous system (fight and flight) and parasympathetic nervous system (rest, balancing)
The vegetative – autonomic – nervous system is divided into two control circuits: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system puts the body in a heightened state of readiness in stressful and dangerous situations. It then releases more stress hormones. They trigger an immediate state of alert: Attention and concentration are increased, muscles are tensed, blood pressure and heart rate are raised and the body’s energy reserves are mobilized. If the body is constantly under tension or stress, the sympathetic nervous system reacts almost non-stop and drives the body and psyche into a state of exhaustion.
The stress hormone cortisol is then released, which causes nerve cells to die in the long term and weakens the immune system. As the body no longer has time to regenerate, illnesses occur. Tension occurs, the immune system is weakened, pain, depression, anxiety and burn-out syndrome develop.
You can counteract this with autogenic training by supporting the parasympathetic nervous system.
This predominantly influences bodily functions that serve the regeneration of the body and the building of energy reserves. Under its influence, repair processes are carried out, and the body’s internal balance is restored. Through autogenic training, individual bodily functions can also be specifically regulated, for example, the heartbeat in stage fright or the blood vessels in hypertension. With this ability, many complaints can already be alleviated.
Through conscious concentration on one’s own body, a feeling of deep calmness arises, and the entire organism can recover.
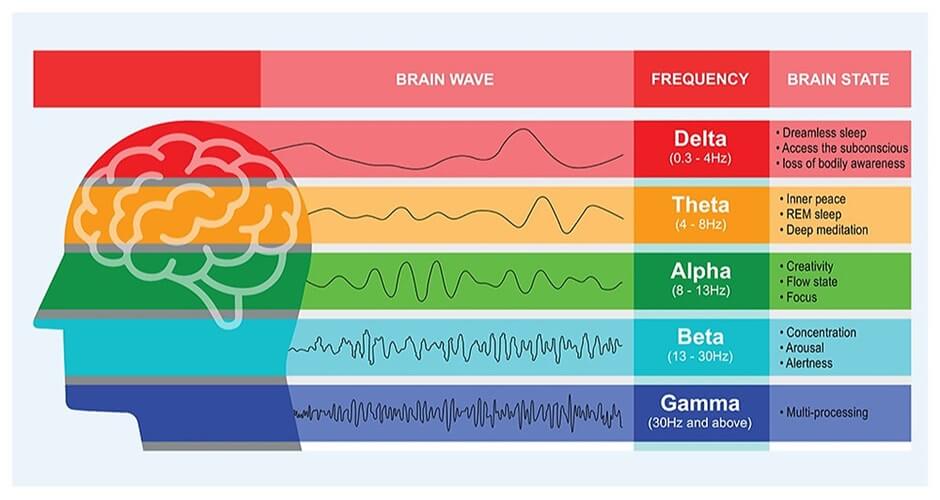
How do brain waves change during autogenic training?
While in the waking state, beta waves dominate our brain, autogenic training puts our brain into alpha waves: thus, into a state where all senses are consciously perceived, but the mind is switched off.
Through consistent practice of autogenic training, we enter the theta state: a deep trance state occurs – similar to deep meditation: the vivid imagination is activated, similar to in REM sleep.”
You can counteract this with autogenic training by supporting the parasympathetic nervous system.
TIP
What can I do when I feel exhausted?
If you’ve been feeling exhausted for weeks or months:
- Try to sit with your eyes closed for at least 10-15 minutes, 1-2 times a day, and focus on your breathing and introspect.
- Ask yourself in this meditative state what you really need to find your peace again.
- Check your thoughts and make a list to see where you’re directing your attention.
- Schedule appointments for yourself in your calendar and do what truly brings you joy.
Are you interested in the information mentioned above?
Do you want to try out the method?
If you would like to not only learn about Autogenic Training but also experience it firsthand, then come by and schedule a free 30-minute consultation where we can discuss whether this method is suitable for you.